Knee Arthroscopy
The ideal way to repair a damaged knee has always been a procedure that does not require cutting into the sensitive knee joint. It is therefore not surprising that the look into the joints using optical instruments was a foremost goal already 100 years ago. The technique known as arthroscopy or arthroscopic surgery was vastly advanced at the beginning of the 1990s and has since then become an unparalleled success. Today arthroscopy is an indispensable procedure in modern knee surgery.
What does knee arthroscopy mean?
Arthroscopy comes from the Greek language and literally translated it means “arthron – joint” and “skopein – to look into”. Today arthroscopy does not only mean to look into the knee joint, but it also stands for the simultaneously conducted minimally invasive repair of a joint damage.
What are the procedures in a knee arthroscopy?
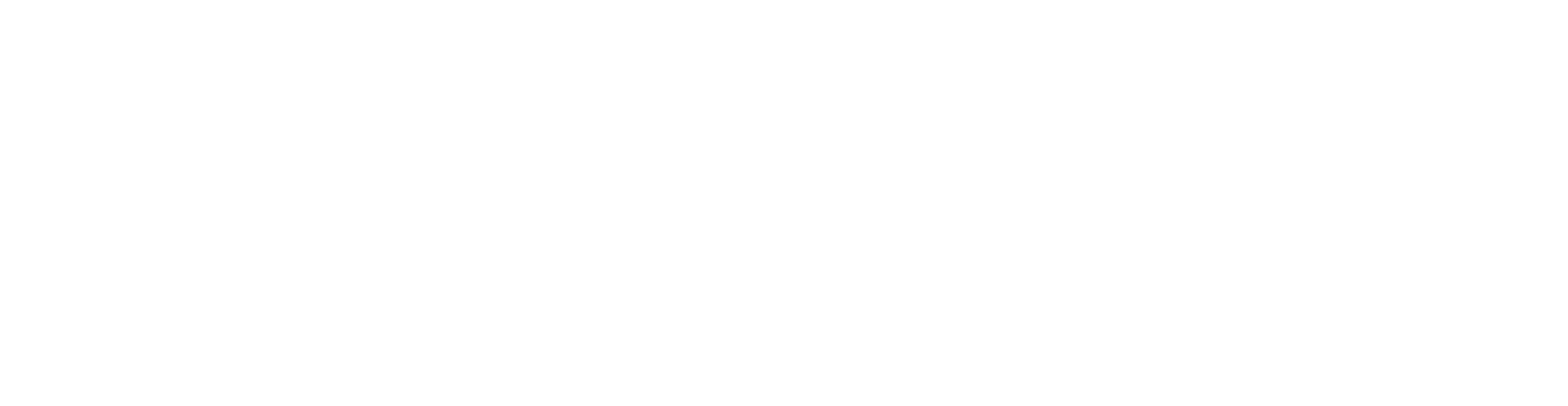
In a knee arthroscopy usually only two small incisions, about 3 mm in size are necessary to perform the operation. Through one of these incisions, a small optical system (endoscope) is inserted into the knee joint with a miniature camera. The camera displays the inside of the joint with all the important structures (meniscus, cruciate ligament, cartilage, etc.) on a monitor to guide the surgeon in the procedure. The surgeon also uses these miniature instruments to inject physiological saline into the joint. The joint is than rinsed to remove any cartilage debris present in the joint.
Through the second 3 mm-incision, the surgeon inserts special surgical instruments into the knee joint to repair any damage present in the joint. These instruments are mechanical instruments such as miniature scissors, electro-thermal or laser-like instruments.
What are the advantages of a knee arthroscopy?
When performing an arthroscopy, the experienced surgeon can accurately assess any damage in the knee joint with the mini camera and at the same time treat the joint in the most optimal manner. Because of the enlarged optics, an experienced surgeon can perform such a surgery with utmost precision.
Advantageous over a surgery with a large incision and complete opening of the knee joint, is that in an arthroscopy healthy structures do not have to be injured while repairing the joint damage. Thus, for the patient knee arthroscopy is less stressful and less painful than open surgery. After arthroscopy, the knee joint recovers rapidly and is soon fully functional again. Minor arthroscopic surgery as a meniscus surgery can possibly be carried out on an outpatient basis. Larger arthroscopic surgeries such as a cruciate ligament surgery, is usually associated with a short hospital stay of about 2 to 3 days.
In a knee arthroscopy general surgical risk such as infection, bleeding, nerve injury, joint stiffness, thrombosis, etc. are usually significantly lower than in an open knee surgery.
What are the risks of a knee arthroscopy
Prior to any surgery, including a knee arthroscopy, the type and extend of the damage in the knee joint must be accurately assessed. In addition, a knee specialist has to determine whether the joint damage can be fully repaired by arthroscopy or whether consequential damages such as the development of osteoarthritis can at least be minimized. The medical history of the patient, an extensive physical examination by an orthopedic knee specialist, and possibly additional laboratory examinations such as X-ray, ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evaluations are necessary to fully assess the patient’s condition.
Even a minimally invasive surgery like knee arthroscopy must be performed with great caution – after all, minimally invasive or not, surgery is surgery. Although, the risk of arthroscopy surgery is comparatively small, complications can never be excluded 100%.
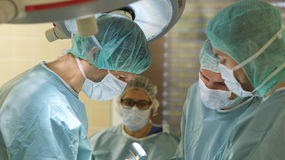
Of major importance for the success of a knee arthroscopy is certainly the experience of the surgeon and his/her team.
Anesthesia - knee joint arthroscopy
An arthroscopy of the knee joint requires anesthesia. Today an arthroscopy of the knee is performed most often under a short general anesthesia. Due to the progress made in recent years, medically, technically and pharmacologically, general anesthesia is the best tolerated pain relief. However, this procedure should be individually decided upon by the anesthetist after appropriate examination of the patient.
Post-operative treatment - knee joint arthroscopy
Even with a minimally invasive procedure like an arthroscopy of the knee joint, an adequate treatment for the healing success is crucial for a complete recovery. The treating physician, i.e. surgeon, should discuss all treatment procedures with the patient prior to the surgery. As a rule, crutches are required for a few days to prevent strains after the arthroscopy. Targeted physiotherapy is another supportive measure to speed up the recovery process.
Important issues related to a knee arthroscopy
The following questions should be discussed between the surgeon and the patient prior to an arthroscopy of the knee:
- What damage is present in the knee?
- Can the damage be repaired by arthroscopy or can a progression of the damage be prevented?
- Are there other treatment methods than an arthroscopy?
- How much experience does the surgeon have with this kind of surgeries?
- Can arthroscopy be performed on an outpatient basis or is a hospital stay required?
- How long do I have to walk on crutches?
- When will I be able to work again?
- How often do I have to go to physiotherapy?
- What can I do myself to contribute to a successful treatment?
- When can I resume my sports activities?
A knee arthroscopy should be performed only by very experienced knee specialists.
Specialists: Arthroscopy Knee Joint
For an optimal arthroscopic surgery of the knee joint, the knee and shoulder experts at the Klinik am Ring are particularly well-qualified.Stefan Preis, M.D. and Jörg Schroeder, M.D., senior physicians at the Practice and Department of Orthopedics and Sports Traumatology at the Klinik am Ring in Cologne, specialize together with their team in the treatment of knee and shoulder disorders. In 2004, they founded the WEST GERMAN SHOULDER KNEE & CENTER, Cologne. The team consisting of eight specialists treats more than 10,000 patients per year. The team performs more than 2,500 surgeries annually, of which are about 800 arthroscopic surgeries of the knee joint.